6 Things You Should Know About Fragment URLs
![]() March 1, 2011 in
HttpWatch
March 1, 2011 in
HttpWatch
1. A Fragment URL Specifies A Location Within A Page
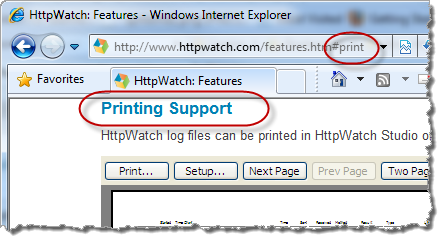
Any URL that contains a # character is a fragment URL. The portion of the URL to the left of the # identifies a resource that can be downloaded by a browser and the portion on the right, known as the fragment identifier, specifies a location within the resource:

In HTML documents, the browser looks for an anchor tag <a> with an id attribute matching the fragment. For example, in the URL shown above the browser finds a matching tag in the Printing Support heading:
Printing Support
and scrolls the page to display that section:
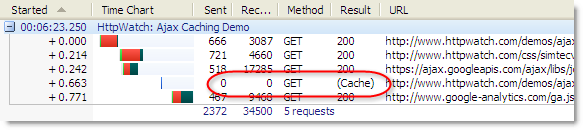
2. Fragments Are not Sent in HTTP Request Messages
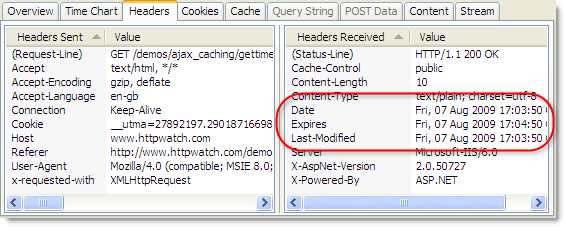
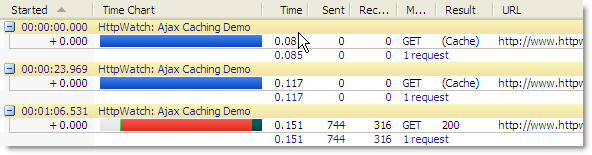
If you try using fragment URLs in an HTTP sniffer like HttpWatch, you’ll never see the fragment IDs in the requested URL or Referer header. The reason is that the fragment identifier is only used by the browser – it doesn’t affect which resource is returned from the server.
Here’s a screen shot of HttpWatch showing the traffic generated by refreshing a fragment URL:
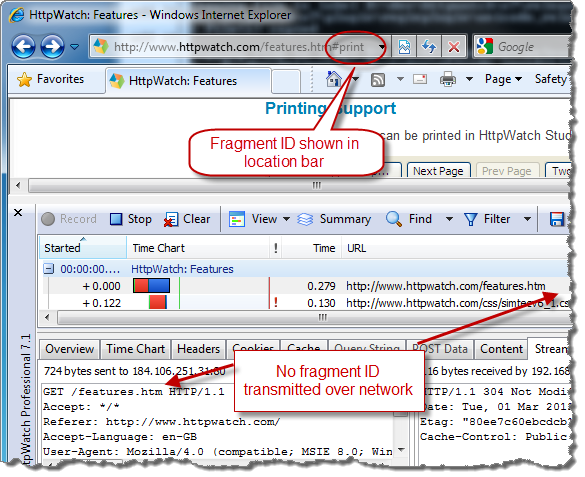
So don’t expect to see fragments identifiers in your server side code.
3. Anything After the First # is a Fragment Identifier
It doesn’t matter if the first # appears to be contained within the host name, path or query string – it always indicates where the fragment identifier starts.
For example, here’s a URL that attempts to encode an HTML color and shape into the query string:
http://example.com/?color=#ffff&shape=circle |
Unfortunately, the # in the HTML color makes the rest of the URL a fragment identifier and the server will see a single, empty color parameter in the query string:
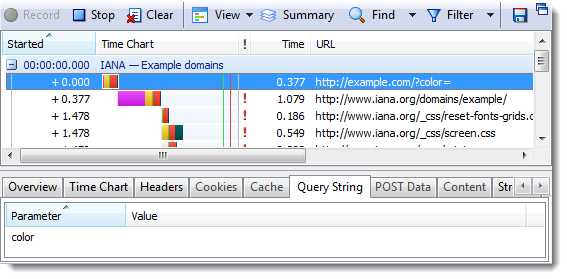
4. Changing A Fragment ID Doesn’t Reload a Page but Does Create History
Fragments have a couple of handy features. First, if you manually change a fragment URL from something like this:
http://www.httpwatch.com/features.htm#filter |
to this:
http://www.httpwatch.com/features.htm#print |
and the browser scrolls the page to the new location but doesn’t reload the page.
However, it does add an entry in the browser’s history so that clicking the Back button will go back to the original location in the page.
These features are particularly useful when used with JavaScript (see below) to create linkable URLs and history for pages that either use top level HTML frames or update their content dynamically with Ajax calls.
5. JavaScript Can Use window.location.hash to Change Fragment IDs
The window object’s hash property allows JavaScript to manipulate the current page’s fragment identifier. As described in 4) this can be used to add history entries for a page without forcing a complete reload.
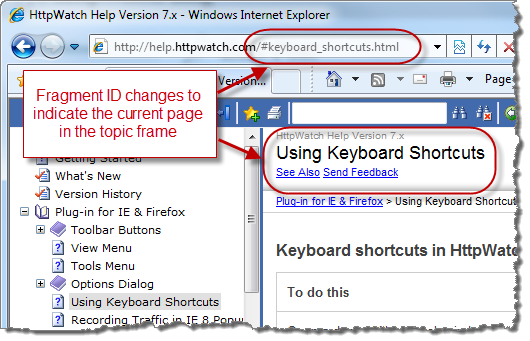
We recently deployed the help and automation reference for HttpWatch on our web site using the frame based HTML generated by the help authoring tool. Although the content was easily accessible in the browser, the URL in the location bar didn’t change as you moved between topics making it practically impossible to share URLs for topics of interest.
The solution was to use fragment identifiers and JavaScript to create linkable URLs. The fragment identifier specifies the embedded help topic page:
6. Googlebot Ignores Fragments By Default
The Googlebot is responsible for crawling sites to find content and embedded links that will become part of the Google search index. It fetches and parses HTML, but it’s not a full blown browser and doesn’t have a JavaScript engine. As a consequence, it will normally ignore fragment identifiers and just look at the resource returned from the web server. Any JavaScript used by your page to load or build content will not be executed.
This means it would be impossible for Ajax driven sites to be indexed and have their fragment URLs returned directly in Google searches. To overcome this problem Google supports a convention that allows the Googlebot to turn fragment identifiers into query string parameters.
To use this indexing scheme you would first need to change all your fragment identifiers to start with a ! symbol:
http://www.example.com/ajax.html#mystate |
would need to change to:
http://www.example.com/ajax.html#!mystate |
The presence of the leading ! indicates to Google that you support this scheme.
Also, your page needs to be able supply the HTML for a given state in response to a query string parameter named _escaped_fragment_ . When the Googlebot needs the content for a given state it supplies the fragment identifier using a simple GET request and a query string value:
http://www.example.com/ajax.html?_escaped_fragment_=mystate |