How to use Selenium automation with HttpWatch and Chrome
![]() January 11, 2018 in
Automation , C# , Chrome , HttpWatch
January 11, 2018 in
Automation , C# , Chrome , HttpWatch
The HttpWatch automation interface provides programmatic control of HttpWatch in both IE and Chrome browsers. It can be used to develop tests in almost any programming language (e.g. C#, JavaScript, Ruby, etc) that capture low level network timings, errors and other statistics generated when a web page is accessed.
However this interface only provides a basic GotoURL method to navigate between pages. If your testing requires more interaction, for example submitting forms or clicking on buttons, we recommend using the Selenium automation framework. The latest HttpWatch update (version 11.1.19) includes several Selenium related improvements to make the integration even easier:
- A new form fill C# code example using Selenium and Chrome
- A new Chrome.HttpWatchCRXFile property making it easier to load the HttpWatch extension in the Selenium Chrome session
- The Selenium based C# code examples now use Nuget packages to automatically install and configure the Selenium libraries required for Chrome and IE
In Visual Studio you no longer the need to separately download and install Selenium. Simply add these two Nuget packages to your project:
- Selenium.WebDriver – the .NET language bindings for Selenium
- Selenium.WebDriver.ChromeDriver – the Selenium driver for Chrome
Once you’ve done this, Selenium will be automatically downloaded and installed when you build your project. It also makes maintenance easier as Visual Studio will show you when updates to these packages are available.
Starting a session using both HttpWatch and Selenium in Chrome requires just a few simple steps. The first is creating Selenium with the HttpWatch extension installed:
Controller control = new Controller(); // Make sure the HttpWatch extension is enabled in the Selenium Chrome session by referencing the CRX file // e.g. C:\Program Files (x86)\HttpWatch\HttpWatchForChrome.crx // The HttpWatchCRXFile property returns the installed location of the CRX file var options = new ChromeOptions(); options.AddExtension(control.Chrome.HttpWatchCRXFile); // Start the Chrome browser session var driver = new ChromeDriver(options); // Goto blank start page so that HttpWatch recording can be started driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("about:blank"); |
The new HttpWatchCRXFile property saves you having to hard code a path to the HttpWatch installation on your PC.
The next step is attaching HttpWatch to the instance of Chrome created by Selenium. This is achieved by setting a unique page title and then calling the AttachByTitle method:
// Set a unique title on the first tab so that HttpWatch can attach to it var uniqueTitle = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(); driver.ExecuteScript("document.title = '" + uniqueTitle + "'"); // Attach HttpWatch to the instance of Chrome created through Selenium Plugin plugin = control.AttachByTitle(uniqueTitle); |
Once everything is setup you can use Selenium methods to interact with controls on the page and HttpWatch methods to control recording and lookup the required network level data or timings:
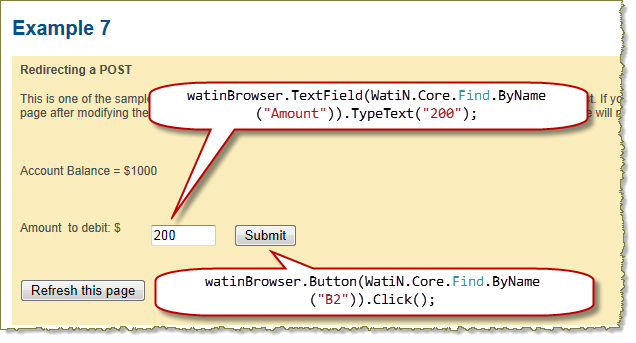
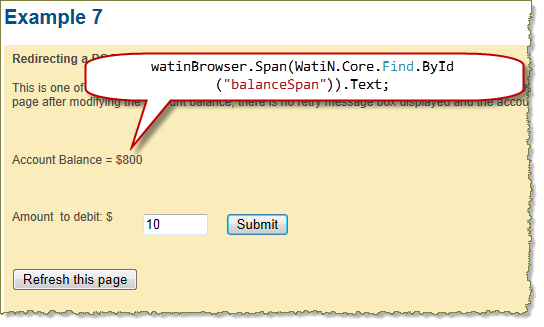
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl(url); // Start recording now that page containing the form is loaded plugin.Log.EnableFilter(false); plugin.Clear(); plugin.Record(); // Put 200 in the amount field driver.FindElement(By.Name("Amount")).Clear(); driver.FindElement(By.Name("Amount")).SendKeys("200"); // Click on the submit button driver.FindElement(By.Name("B2")).Click(); Console.WriteLine("\r\nClicked on submit button..."); // Use the HttpWatch Wait call to ensure HTTP activity has ceased control.Wait(plugin, -1); // Stop recording HTTP plugin.Stop(); // Read the updated account balance back from the page string accountBalance = driver.FindElement(By.Id("balanceSpan")).Text; if (plugin.Log.Pages.Count != 0) { Console.WriteLine("\r\nPage Title: '" + plugin.Log.Pages[0].Title + "'"); Console.WriteLine("\r\nNew account balance: " + accountBalance ); Console.WriteLine(); // Display summary statistics for page Summary summary = plugin.Log.Pages[0].Entries.Summary; Console.WriteLine("Total time to load page (secs): " + summary.Time); Console.WriteLine("Number of bytes received on network: " + summary.BytesReceived); Console.WriteLine("HTTP compression saving (bytes): " + summary.CompressionSavedBytes); } // Need to use Selenium Quit to correctly shutdown Selenium and browser driver.Quit(); |
You can read more about the Selenium and Chrome sample code in the HttpWatch Automation documentation.