In December 2009, Google launched the asynchronous version of the Google Analytics script. The update aimed to address potential script blocking problems that have been extensively researched and reported by Steve Souders at Google.
Steve’s blog post about the new asynchronous loading of Google Analytics identified three potential benefits:
- Your pages should load faster
- Availability or performance problems at Google should have less impact on your site
- Analytics data is more likely to be collected if a user leaves a page early
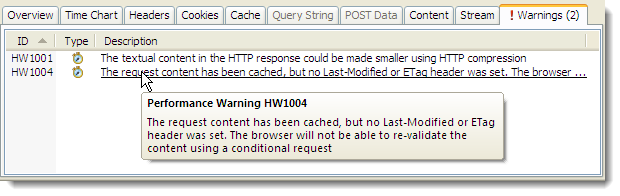
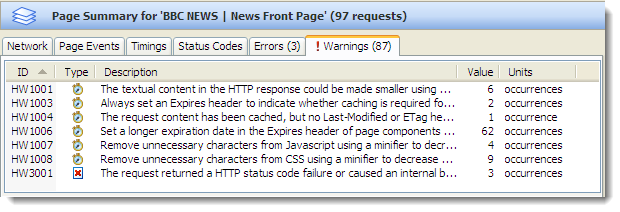
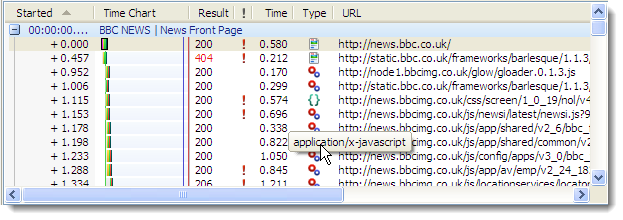
Before applying the change to our web site we decide to compare the new and old versions of the Google Analytics scripts using HttpWatch 7.0 .
The following sections describe what has changed in the asynchronous Google Analytics script and the tests we performed to compare it to the traditional synchronous version.
What has Changed?
Google Analytics collects data using two components on a page:
- A javascript file script file that is loaded from http://www.google-analytics.com/ga.js
- A 1×1 pixel image beacon (http://www.google-analytics.com/__utm.gif) that passes data back to Google in query string parameters
You enable Google Analytics on a web page by calling a page tracking function in ga.js. This function automatically gathers analytics data, such as operating system and browser versions, then generates the call to the image beacon.
The difference between the two ways of loading Google Analytics is in the way that the script file is loaded. In the traditional synchronous version, two small script tags are added at the end the page’s <body> tag:
...
<script type="text/javascript">
var gaJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ?
"https://ssl." : "http://www.");
document.write(unescape("%3Cscript src='" + gaJsHost +
"google-analytics.com/ga.js' type='text/javascript'%3E%3C/script%3E"));
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("XX-XXXXXX-X"); // Your GA id
pageTracker._trackPageview();
</script>
</body>
... |
...
<script type="text/javascript">
var gaJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ?
"https://ssl." : "http://www.");
document.write(unescape("%3Cscript src='" + gaJsHost +
"google-analytics.com/ga.js' type='text/javascript'%3E%3C/script%3E"));
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("XX-XXXXXX-X"); // Your GA id
pageTracker._trackPageview();
</script>
</body>
...
The first script tag ensures that the correct HTTP or HTTPS version of the qa.js file is loaded. The second script tag then calls into the javascript file triggering the beacon image download.
These two script tags are placed at the end of the body tag to ensure that they don’t hold up the download of any other resources on the page. The disadvantage of doing this is that the analytics call may not be triggered if the user exits the page before it has completely downloaded.
The asynchronous version of the Google Analytics loading code uses a single script tag at the end of the page’s <head> :
...
<script>
var _gaq = _gaq || [];
_gaq.push(['_setAccount', 'XX-XXXXXX-X']);
_gaq.push(['_trackPageview']);
(function() {
var ga = document.createElement('script');
ga.type = 'text/javascript';
ga.async = true;
ga.src = ('https:' == document.location.protocol ? 'https://ssl' : 'http://www')
+ '.google-analytics.com/ga.js';
var s = document.getElementsByTagName('script')[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(ga, s);
})();
</script>
</head>
... |
...
<script>
var _gaq = _gaq || [];
_gaq.push(['_setAccount', 'XX-XXXXXX-X']);
_gaq.push(['_trackPageview']);
(function() {
var ga = document.createElement('script');
ga.type = 'text/javascript';
ga.async = true;
ga.src = ('https:' == document.location.protocol ? 'https://ssl' : 'http://www')
+ '.google-analytics.com/ga.js';
var s = document.getElementsByTagName('script')[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(ga, s);
})();
</script>
</head>
...
It sets up the parameters required to make the call into ga.js but doesn’t invoke the function directly. A script element is added to the document allowing asynchronous download without blocking other elements of the page. The HTML 5 async attribute is also set on the script tag for browsers that support it.
Once the ga.js file is loaded and executed it looks for an array variable called _gaq and executes the function with the previously specified arguments.
Do Pages Load Faster With Asynchronous Google Analytics?
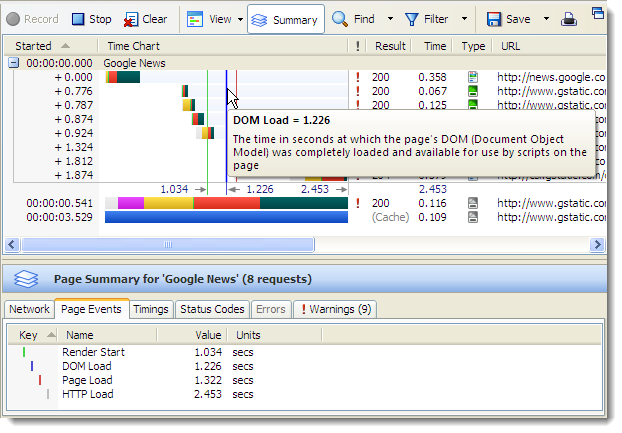
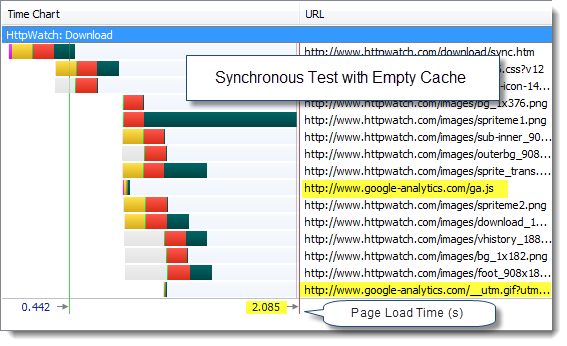
To try this out we created a version of our Download page using both versions of the Google Analytics loading code. We first tried the synchronous version with an empty cache in IE to simulate a new visitor to the page:
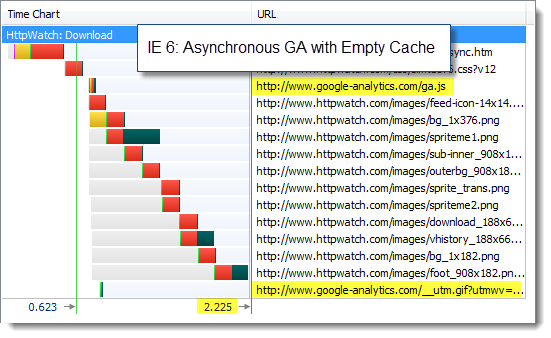
And then with the asynchronous version:
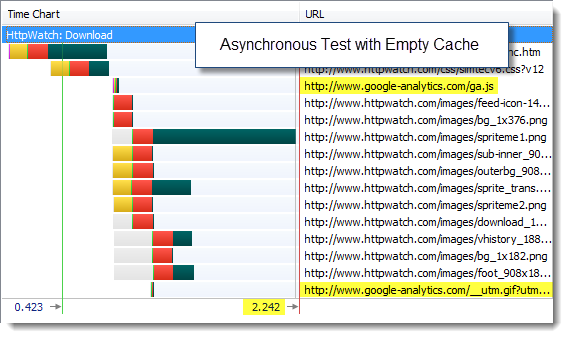
The page load times were dominated by other components on the page. Using the asynchronous version of Google Analytics didn’t really make any difference.
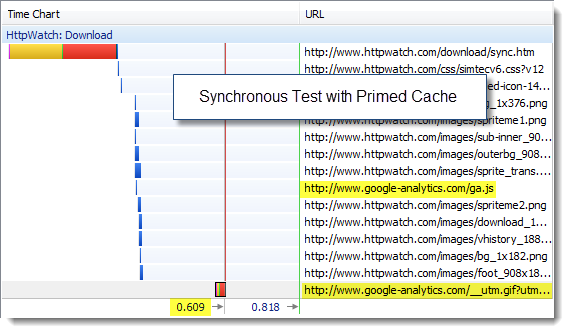
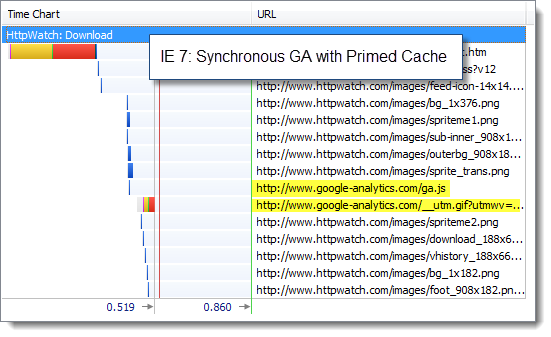
We tried the same tests with a primed cache to see if there would be a greater impact when the page was loaded during a repeat visit. First the synchronous version:
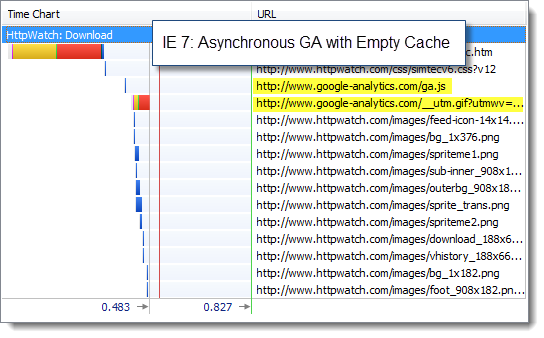
and then the asynchronous version:
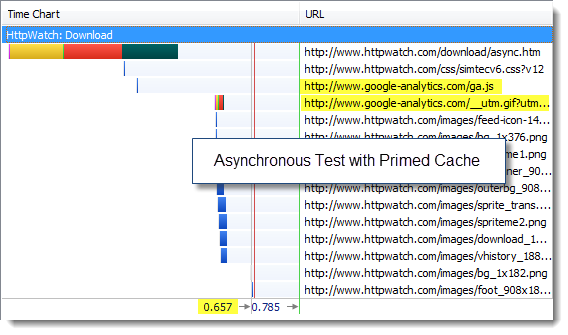
Again there was practically no difference in the page load time of the page allowing for variability in our tests.
The reason for that is that calls to Google Analytics are incredibly fast (usually around a 100ms or less) and the download of the image beacon doesn’t block other components because it uses a different hostname.
We tried Firefox 3.6 and got almost the same results.
Conclusion: Google Analytics is so fast that you won’t see any significant improvement with the asynchronous loading version.
Would Google Performance Problems Have Less Impact With Asynchronous Google Analytics?
For this test we needed to simulate performance problems at Google. We did this by modifying the standard script snippets to call our own ASP.NET versions of the Google files that served the same content but added a 5 second delay.
For example, here’s the ASPX file we used to serve up a local copy of ga.js:
<%@ Page Language="C#" Debug="true" %>
<%@ Import Namespace=System.IO %>
<%
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(6000);
Response.AddHeader("Content-Type", "text/javascript");
Response.WriteFile( ".\\ga.js");
Response.End();
%> |
<%@ Page Language="C#" Debug="true" %>
<%@ Import Namespace=System.IO %>
<%
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(6000);
Response.AddHeader("Content-Type", "text/javascript");
Response.WriteFile( ".\\ga.js");
Response.End();
%>
We did something similar with the Google __utm.gif file so that we could add delays to either component.
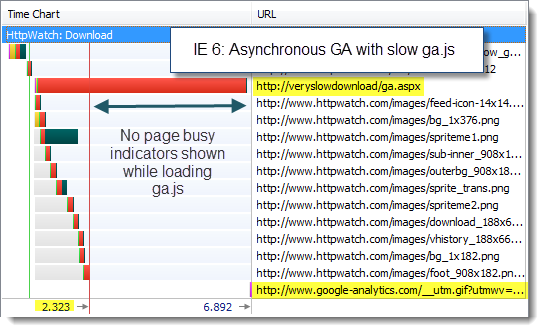
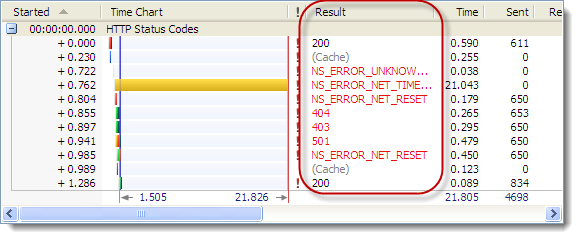
Using our slow simulation of ga.js in IE 8 we found that the page’s onload event was delayed with the synchronous version of the Google Analytics:
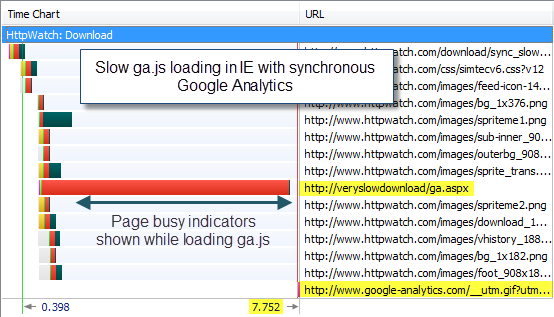
This caused the IE 8 to display the spinning icon in the current tab:
and a “Waiting…” message in the status bar:

indicating to the user that the page was not fully downloaded.
We then tried using the slow version of the __utm.gif image file. This didn’t cause a problem in IE 8 as the page loaded successfully but continued to download the image beacon in the background even with the synchronous version of Google Analytics:
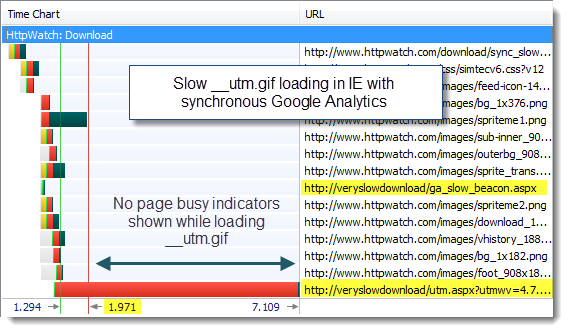
Firefox 3.6 didn’t cope as well. Delaying the download of the beacon file with the synchronous loading code had the same effect as delaying the ga.js file – the page load was delayed, the spinning tab icon was displayed and the status line indicated that it was waiting for data.
We then tried the asynchronous version of the analytics loading code. Delaying either the ga.js or utm.gif file had no effect on the loading of the page in IE; effectively hiding the issue from the web site visitor:
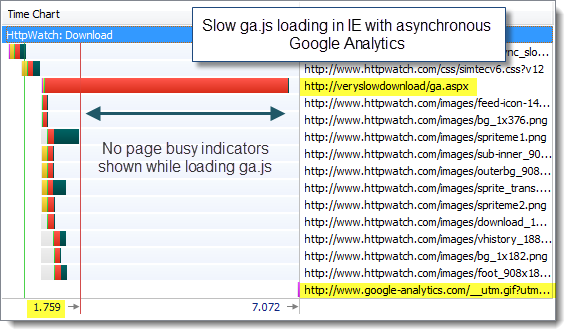
Surprisingly, the asynchronous version of the analytics code made no difference to Firefox 3.6 when we simulated slow downloads of the Google components:
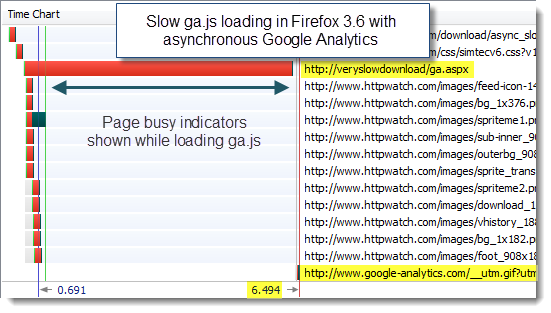
Conclusion: Using the asynchronous load made IE 8 more robust to performance problems in the loading of qa.js. Otherwise it made no difference. In reality, ga.js is often cached anyway making it the less likely of the two components to be subject to performance problems.
Is Data More Likely to be Recorded by Asynchronous Google Analytics During Early Page Exits?
To test this potential benefit we changed our test pages to include a slow loading script file at the top of the body tag. The idea was to emulate what might happen on your page if a third party component, such as an ad script, started to slow down.
The script tag we added called an ASPX file than delayed 6 seconds before returning an empty script block:
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src='http://veryslowdownload/ad.aspx'></script> |
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src='http://veryslowdownload/ad.aspx'></script>
This stopped our page being displayed for six seconds.
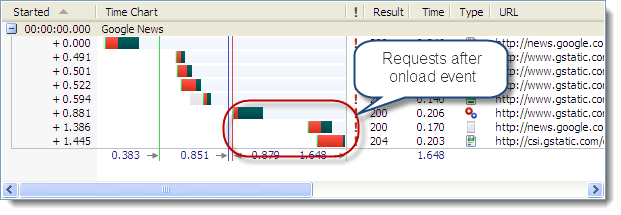
Using the synchronous version of the loading code in IE 8 and Firefox 3.6, we found that the Google Analytics beacon image was not downloaded if the user gave up and went elsewhere:
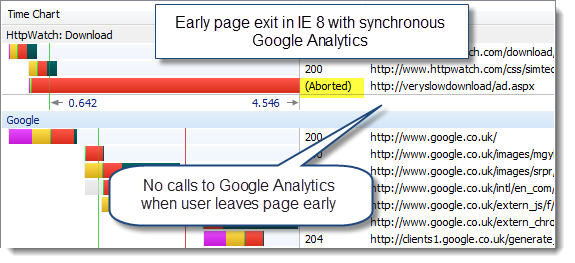
The asynchronous loading of Google Analytics solved this problem in both browsers. The image beacon was downloaded almost immediately even though the page was blocked by the slow script tag:
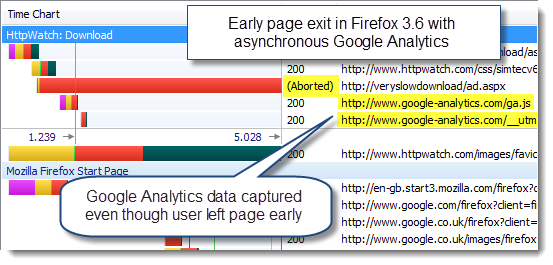
Conclusion: The asynchronous version of Google Analytics helps to ensure that analytics data is gathered in IE and Firefox when the user leaves a page early.
Should I Use the Asynchronous Version of Google Analytics?
Yes, but not for the reasons you might expect. It’s unlikely to make any difference to how quickly your pages load.
The main reason to use it is that you are more likely to get analytics data if a user leaves a page early.
![]() August 12, 2010 in
HttpWatch , Javascript , Optimization
August 12, 2010 in
HttpWatch , Javascript , Optimization 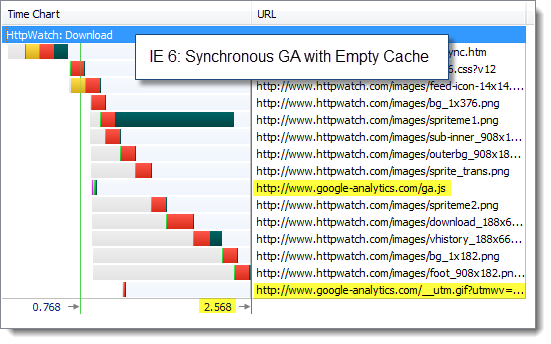
![]()